
Workforce Innovation and Opportunity Act
Created by federal law in 2014, the Workforce Innovation and Opportunity Act streamlines the workforce development system to offer services to support the individual as a whole resulting in successful employment in the competitive labor market. In Wisconsin, WIOA encompasses four Titles and two partner programs. The Department of Workforce Development, or DWD, is the state’s federally‐designated workforce agency and is therefore, responsible for the overall implementation of WIOA. The Wisconsin Technical College System is specifically responsible for implementing the Adult Basic Education Program and English Language Learner Program, or Title II of the law.
A primary goal for WIOA in Wisconsin is to deliver seamless, customer‐focused, integrated services across all WIOA Titles and partner programs.
This program helps people find employment and may fund training when needed for an individual to gain or retain employment.
The Adult Program serves people who are at least 18 years old and (if applicable) registered for Selective Service.
The Dislocated Worker Program serves individuals (if applicable) registered for Selective Service who have lost their jobs and who fit into one of the dislocated worker categories defined in WIOA.
The Youth Program serves in-school youth (ages 14-21) and out-of-school youth (ages 16-24) who need assistance with training or education to enter the workforce successfully. The focus is on young people with barriers to success.
A participant is someone eligible for one of the Title 1 programs who has received a service that DOL defines as "participation-causing." These are training and career services that require personalized attention from a career planner.
A reportable individual is one who has taken some action demonstrating an intent to use workforce development program services and who has met specific reporting criteria, including:
The Wisconsin Technical College System’s Adult Education programs are designed to support adult learners in their academic pursuits, career advancement and English language proficiency. The programs serve a diverse range of students needs including those seeking to obtain a high school credential, improve their job prospects, or enhance English skills. All Adult Education programming is free or low cost.
Adult Education programs at the Wisconsin Technical College System and some community-based organizations receive substantial support from the federal Adult Education and Family Literacy Act (AEFLA) Title II funding. This funding enables the colleges to equip adult learners with the necessary skills to succeed in various educational and employment endeavors.
Title II Programs help adult learners:
An eligible individual is a person who:
For further details or inquiries about Title II funding, please reach out to: Christina Lorge, Associate Vice President of Student Success at christina.lorge@wtcsystem.edu.
WTCS Adult Education program encompasses several key categories:
Tailored instruction to meet learners’ educational needs, aiding in GED or high school equivalency diploma (HSED) attainment and facilitating successful transition to post- secondary education.
Programs designed to assist multilingual adults in achieving English proficiency, leading to secondary school attainment and/or facilitating transitions to further education or employment.
Comprehensive programming incorporating elements of Adult Education, ELL and occupational skills training, aimed at reducing recidivism and increasing employment opportunities for justice-involved individuals.
Each college offers a comprehensive array of programs (mental health counseling, disability accommodations, emergency assistance and much more) and courses to help students reach their educational and professional goals. Additionally, each one provides a variety of services to support a student’s overall development and growth. These services are free to access for enrolled students and can be critical to a student’s persistence and success.
Services and eligibility may vary from college to college. The best strategy for identifying student services and educational programming at a particular college is to visit the college website. This link will take you to a general college page and you will need to use the search bar to locate the information you are searching for.
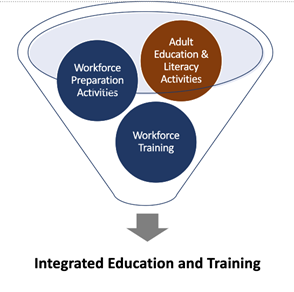
Many colleges offer IET programs which are funded through Title II. This programming has emerged as a service approach to help individuals acquire basic skills while pursuing occupational or industry-specific training. Through an IET model, participants receive simultaneous instruction in basic skills such as math, reading, or spoken English, as well as workforce training and workforce preparation.
Collectively, IET programming has the potential to:
Many IETs are listed in the ETPL. You can also check with the Adult Education department at the technical college of your choice for more information on their IET programs.
Job Service provides job search services to job seekers and recruitment assistance to employers through a statewide network of Job Centers and online at https://jobcenterofwisconsin.com/.
A participant is any reportable individual who has received a Basic Career-Staff Assisted service or an Individualized Career Service from Job Service staff.
A reportable individual is one who has taken some action demonstrating an intent to use workforce development program services and who met has specific reporting criteria, including:
Are you working with someone who has a known or suspected disability, and that disability is making it difficult for them to find a job, keep a job, or get a better job? Refer them to the Division of Vocational Rehabilitation (DVR)!
DVR has offices around the state with qualified staff and licensed counselors who connect people to work-related supports and services. DVR can fund support services to help them achieve an appropriate career goal.
It does not matter how much money someone makes to receive DVR services.
To get started, someone can complete the DVR Referral Form for themselves, or on behalf of someone else (with their permission). www.dwd.wisconsin.gov/dvrreferral
Individuals with disabilities, their guardians, or someone supporting the individual can complete a referral form online at dwd.wisconsin.gov/dvr/referral/. An individual may also visit their local DVR office or call or email our main office to have a referral form sent to them.
A job seeker will be asked questions that will help determine the level of DVR support they need to obtain their job goals. Medical records will be collected.
With DVR staff, they will create an Individualized Plan for Employment (IPE) that will include the services and supports you will need to obtain their career goal.
Services may vary, but they may work with a DVR Service Provider to get the needed training and supports to help them obtain their career goal.
Once they obtain a job, their DVR counselor will monitor their progress for 90 days. When they have reached their job goal and have received the services listed in their employment plan, their DVR case will be closed.
DVR offers services to support Wisconsinites with disabilities to achieve their career goals.
The Trade Adjustment Assistance (TAA) Program helps workers who lose their jobs due to foreign competition, including work being moved outside of the United States. TAA program benefits and services make it easier to move past the disruption caused by your layoff, easier to develop in-demand skills, and easier to land a good-paying, full-time job.
The process begins with a petition, which may be filed by the employees, a union representative, the company itself, or sometimes job center staff. The U.S. Department of Labor reviews the petition and investigates whether jobs have been or will be lost because the company is outsourcing work to another country or losing business because of foreign imports. If the U.S. Department of Labor certifies your group, TAA program benefits and services become available. The next step is for you to complete a TAA program application, so the Wisconsin Department of Workforce Development (DWD) can determine your individual eligibility and provide program benefits and services through the state’s job center locations.
The TAA Program offers several benefits and services to help you prepare for and find a new job:
Each benefit and service has specific eligibility requirements that applicants must meet. Work with your TAA Career Planner to find out which benefits and services meet your needs.
To be eligible for the TAA Program, you must:
To find out more information on how to start the process for your company or to check if your company was certified, visit the DOL Website and search for your company’s name.
The JVSG Program serves two distinct customers: Veterans and Wisconsin employers.
Veteran participants are Veterans with significant barriers to employment, who are served by Disabled Veteran Outreach Staff. Business services and employer outreach are provided to Wisconsin employer participants through local Veteran Employment Staff.
The reportable individual category does not apply to this program. However, for the sake of comparability, a reportable individual is one who provides identifying information but has not risen to the level of participation.
Wisconsin’s Department of Children and Families offers programs to parents and caregivers to help support their family.
Wisconsin Works (W-2) helps parents or caregivers get a job and find a career path. There are many services offered by a Wisconsin Works agency in addition to cash assistance to meet a participant’s interests and needs.
Some services are:
Job Access Loan (JAL) is a no-interest loan of up to $1,600 to help a parent or caregiver get or keep a job. There is no credit check or bank involved with a JAL. A JAL can be paid back over 12 months with a combination of community service and cash.
Emergency Assistance (EA) provides a payment and a connection to resources for families facing a setback due to a housing emergency, including impending homelessness and domestic violence, natural disaster, fire, or an energy crisis.
Each of Wisconsin’s 11 Workforce Development Areas is directed by its own board. All of the coordinated efforts by the partners, including the coordination with the technical college districts, happen within and across these 11 areas.
An important fixture in each workforce development area are the local Job Centers. WIOA established the American Job Centers network to provide both job seekers and employers streamlined access to various government-administered education, training, and employment services. In Wisconsin, there are 53 Job Centers throughout the state, which includes 23 comprehensive and 30 affiliate Job Centers. These Job Centers are where partners, which may include the local technical colleges, WDBs, DVR, Job Service, local school districts, TANF providers, W-2 providers and others, coordinate service delivery.
Each WDB is responsible for overseeing the implementation of the WIOA programs in its respective areas. A local WDB is responsible for making decisions on local policies and procedures, managing its share of the federal WIOA funds, and administering contracts with service providers to run some of the WIOA programs on a day-to-day basis.